
Matplotlib的三维可视化,mplot3d教程。
mplot3d tutorial
Contents
Getting started
An Axes3D object is created just like any other axes using the projection=‘3d’ keyword. Create a new and add a new axes to it of type Axes3D:
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dfig = plt.figure()ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
New in version 1.0.0: This approach is the preferred method of creating a 3D axes.
Note
Prior to version 1.0.0, the method of creating a 3D axes was different. For those using older versions of matplotlib, changeax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')to ax = Axes3D(fig).
Line plots
Axes3D.plot(xs, ys, *args, **kwargs)Plot 2D or 3D data.
Argument Description xs, ys x, y coordinates of vertices zs z value(s), either one for all points or one for each point. zdir Which direction to use as z (‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’) when plotting a 2D set. Other arguments are passed on to
(, , , )
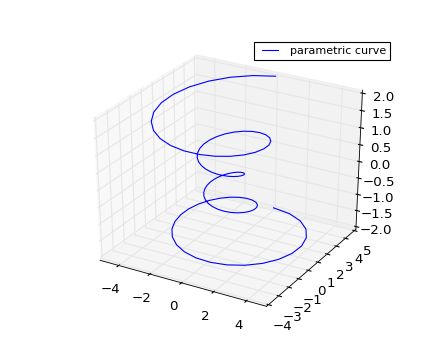
Scatter plots
Axes3D.scatter(xs, ys, zs=0, zdir='z', s=20, c='b', depthshade=True, *args, **kwargs)Create a scatter plot.
Argument Description xs, ys Positions of data points. zs Either an array of the same length as xs andys or a single value to place all points in the same plane. Default is 0. zdir Which direction to use as z (‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’) when plotting a 2D set. s Size in points^2. It is a scalar or an array of the same length as x and y. c A color. c can be a single color format string, or a sequence of color specifications of length N, or a sequence of N numbers to be mapped to colors using thecmap and norm specified via kwargs (see below). Note that c should not be a single numeric RGB or RGBA sequence because that is indistinguishable from an array of values to be colormapped. c can be a 2-D array in which the rows are RGB or RGBA, however. depthshade Whether or not to shade the scatter markers to give the appearance of depth. Default is True. Keyword arguments are passed on to.
Returns a
(, , , )
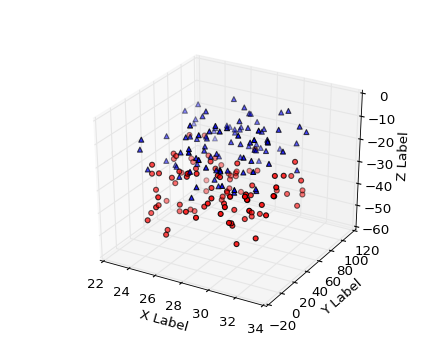
Wireframe plots
Axes3D.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)Plot a 3D wireframe.
The
rstrideandcstridekwargs set the stride used to sample the input data to generate the graph. If either is 0 the input data in not sampled along this direction producing a 3D line plot rather than a wireframe plot.Argument Description X, Y, Data values as 2D arrays Z rstride Array row stride (step size), defaults to 1 cstride Array column stride (step size), defaults to 1 Keyword arguments are passed on to.
Returns a
(, , , )

Surface plots
Axes3D.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)Create a surface plot.
By default it will be colored in shades of a solid color, but it also supports color mapping by supplying the cmapargument.
The
rstrideandcstridekwargs set the stride used to sample the input data to generate the graph. If 1k by 1k arrays are passed in the default values for the strides will result in a 100x100 grid being plotted.Argument Description X, Y, Z Data values as 2D arrays rstride Array row stride (step size), defaults to 10 cstride Array column stride (step size), defaults to 10 color Color of the surface patches cmap A colormap for the surface patches. facecolors Face colors for the individual patches norm An instance of Normalize to map values to colors vmin Minimum value to map vmax Maximum value to map shade Whether to shade the facecolors Other arguments are passed on to
(, , , )
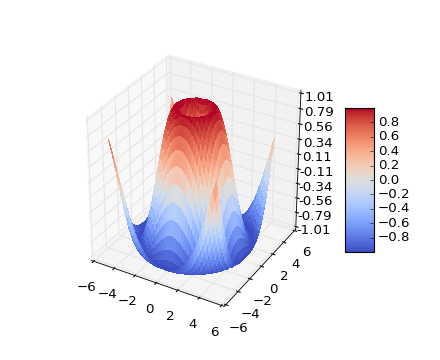
(, , , )

(, , , )
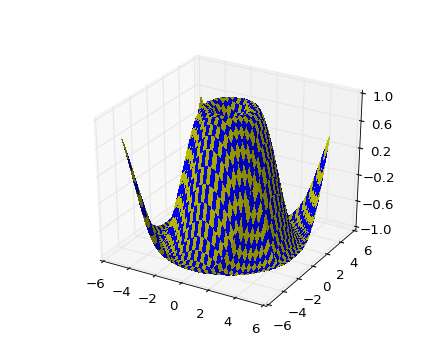
Tri-Surface plots
Axes3D.plot_trisurf(*args, **kwargs)-
Argument Description X, Y, Z Data values as 1D arrays color Color of the surface patches cmap A colormap for the surface patches. norm An instance of Normalize to map values to colors vmin Minimum value to map vmax Maximum value to map shade Whether to shade the facecolors The (optional) triangulation can be specified in one of two ways; either:
plot_trisurf(triangulation, ...)
where triangulation is a object, or:
plot_trisurf(X, Y, ...)plot_trisurf(X, Y, triangles, ...)plot_trisurf(X, Y, triangles=triangles, ...)
in which case a Triangulation object will be created. See for a explanation of these possibilities.
The remaining arguments are:
plot_trisurf(..., Z)
where Z is the array of values to contour, one per point in the triangulation.
Other arguments are passed on to
Examples:
(, , , )

()
(, , )
(, , )
New in version 1.2.0: This plotting function was added for the v1.2.0 release.
(, , , )

Contour plots
Axes3D.contour(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)Create a 3D contour plot.
Argument Description X, Y, Data values as numpy.arrays Z extend3d Whether to extend contour in 3D (default: False) stride Stride (step size) for extending contour zdir The direction to use: x, y or z (default) offset If specified plot a projection of the contour lines on this position in plane normal to zdir The positional and other keyword arguments are passed on to
Returns a
(, , , )

(, , , )
(, , , )
Filled contour plots
Axes3D.contourf(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)Create a 3D contourf plot.
Argument Description X, Y, Data values as numpy.arrays Z zdir The direction to use: x, y or z (default) offset If specified plot a projection of the filled contour on this position in plane normal to zdir The positional and keyword arguments are passed on to
Returns a
Changed in version 1.1.0: The zdir and offset kwargs were added.
(, , , )
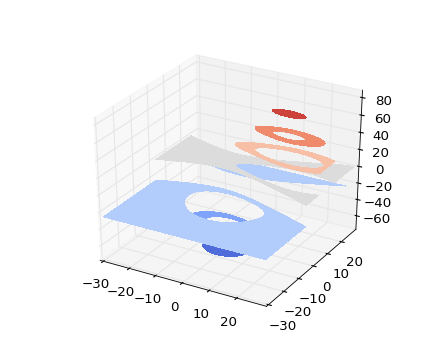
(, , , )

New in version 1.1.0: The feature demoed in the second contourf3d example was enabled as a result of a bugfix for version 1.1.0.
Polygon plots
Axes3D.add_collection3d(col, zs=0, zdir='z')Add a 3D collection object to the plot.
2D collection types are converted to a 3D version by modifying the object and adding z coordinate information.
PolyCollection
LineColleciton
PatchCollection
Supported are:
(, , , )
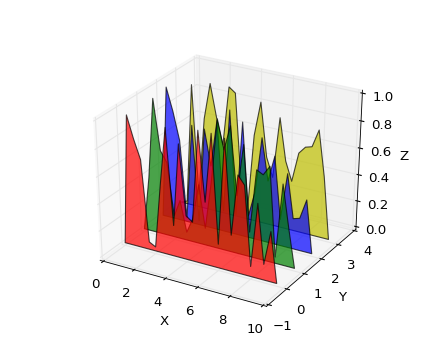
Bar plots
Axes3D.bar(left, height, zs=0, zdir='z', *args, **kwargs)Add 2D bar(s).
Argument Description left The x coordinates of the left sides of the bars. height The height of the bars. zs Z coordinate of bars, if one value is specified they will all be placed at the same z. zdir Which direction to use as z (‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’) when plotting a 2D set. Keyword arguments are passed onto .
Returns a
(, , , )
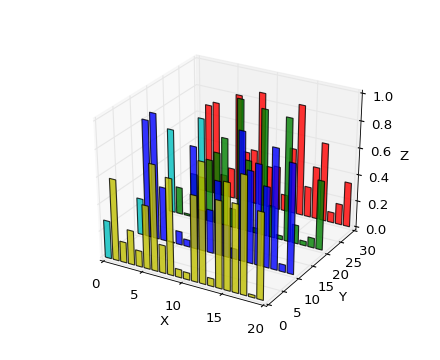
Quiver
Axes3D.quiver(*args, **kwargs)Plot a 3D field of arrows.
call signatures:
quiver(X, Y, Z, U, V, W, **kwargs)
Arguments:
The arguments could be array-like or scalars, so long as they they can be broadcast together. The arguments can also be masked arrays. If an element in any of argument is masked, then that corresponding quiver element will not be plotted.
Keyword arguments:
Any additional keyword arguments are delegated to
length: [1.0 | float]
The length of each quiver, default to 1.0, the unit is the same with the axes
arrow_length_ratio: [0.3 | float]
The ratio of the arrow head with respect to the quiver, default to 0.3
pivot: [ ‘tail’ | ‘middle’ | ‘tip’ ]
The part of the arrow that is at the grid point; the arrow rotates about this point, hence the name pivot.
X, Y, Z:
The x, y and z coordinates of the arrow locations (default is tip of arrow; see pivot kwarg)
U, V, W:
The x, y and z components of the arrow vectors
(, , , )

2D plots in 3D
(, , , )

Text
Axes3D.text(x, y, z, s, zdir=None, **kwargs)Add text to the plot. kwargs will be passed on to Axes.text, except for the
zdirkeyword, which sets the direction to be used as the z direction.
(, , , )
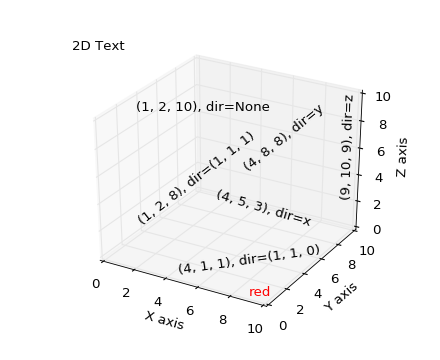
Subplotting
Having multiple 3D plots in a single figure is the same as it is for 2D plots. Also, you can have both 2D and 3D plots in the same figure.
New in version 1.0.0: Subplotting 3D plots was added in v1.0.0. Earlier version can not do this.
(, , , )

(, , , )
